EZ-0024
GPS Module SKU:EZ-0024
Description
The module uses U-BLOX NEO-6M module.The module comes with high-performance ceramic antenna, which is equival of the integrated active antenna.
Module comes with EEPROM. All configuration information can be stored in the EEPROM. A variety of configurations to meet your needs.
The module also comes with a rechargeable backup battery (to support warm or warm start. after the main power supply power off, back-up battery power can maintain a half hour for GPS receiver data stored).
Features
- Use U-BLOX NEO-6M modular, compact, and excellent performance.
- Comes with ceramic antenna, capability of searching star is quite good.
- You can set various parameters via the serial port, and can be stored in the EEPROM, and easy to use.
- Compatible with 3.3V / 5V level, for easy connection to a variety of microprocessor systems.
- built-in rechargeable backup battery, can retentive ephemeris data.
Technical Parameters
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | 3V/5V |
| Model | GPS-NEO-6M-001 |
| Antenna | ceramic antenna |
| Battery | rechargeable battery back-up |
| Signal light | LED light |
| Antenna size | 25*25mm |
| Model size | 25.5mm*31.5mm |
| Mounting Hole | 2mm |
| The default baud rate | 38400 |
| The default output | Compatible with NMEA0183 protocol |
Notice
- Outdoor use
- Note Lightning and waterproof
- Do not support Raspberry Pi 3 B (Because of RPi 3B's serial port problem, it may have other solution)
Package includes:
- 1x GPS module
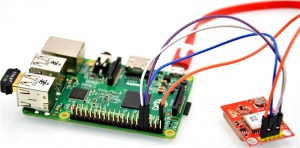
How to wire up
It can be just wire to your Raspberry Pi B/B+/2B's GPIO Pin, TxD and RxD as following picture:
How to use it
1. After power on and login to system. you can open a terminal and typing following command to install packages for GPS module.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install gpsd gpsd-clients python-gps
2.Reboot your Raspberry Pi and login, also typing command in your terminal, it will help you reconfigure your gpsd service:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure gpsd
3. Start the gpsd service:
sudo gpsd /dev/ttyUSB0 -F /var/run/gpsd.sock
4.you can stop the gpsd service:
sudo killall gpsd
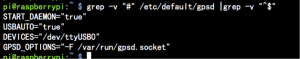
5.You can also use systemctl command to manage this service,but at the first, you should modify the configuration file of gpsd in /etc/default/gpsd,
filling the blank with your device name and socket name and path.
Start service:
sudo systemctl enable gpsd.sock
sudo systemctl start gpsd.sock
Stop service:
sudo systemctl stop gpsd.sock
sudo systemctl disable gpsd.sock
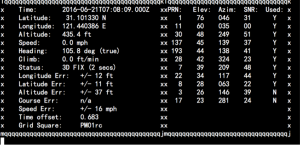
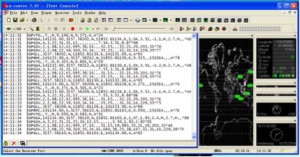
Finally, use this command to get information from GPS module.
sudo cgps -s
You will see this: