D-0006: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 290: | Line 290: | ||
* Control-Any-Devices-Using-Raspberry-PI-and-PCF8574: [ https://www.instructables.com/id/Control-Any-Devices-Using-Raspberry-PI-and-PCF8574/ ] | * Control-Any-Devices-Using-Raspberry-PI-and-PCF8574: [ https://www.instructables.com/id/Control-Any-Devices-Using-Raspberry-PI-and-PCF8574/ ] | ||
* I2C-1602-LCD: [https://github.com/VeggieVampire/I2C-1602-LCD] | * I2C-1602-LCD: [https://github.com/VeggieVampire/I2C-1602-LCD] | ||
==Keywords== | |||
* PCF8574T, LCD1602, driver board, LCD driver board | |||
Revision as of 15:45, 27 March 2020
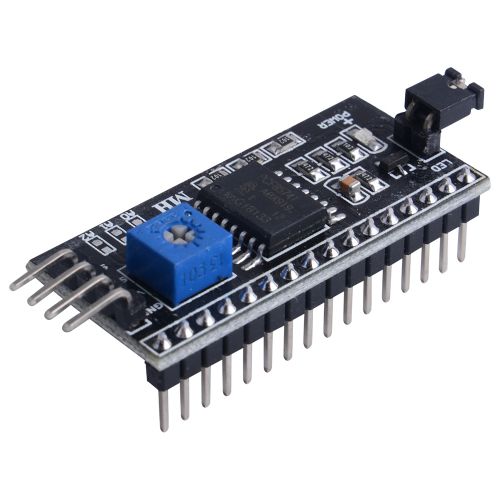
PCF8574T LCD Driver Board
Description
The PCF8574T IO Expansion Board is used as remote 8-bit I/O expander for I2C-bus.
Up to 8 PCF8574T IO Expansion Board can be connected to the I2C-bus, providing up to 64 I/O ports.
The PCF8574T IO Expansion Board features allowing the use of multi module connected to the I2C bus at the same time by connecting the pinheader and connector.
There is a small potentiometer onboard, which can adjust the backlight of LCD1602 or LCD2004, and a jumper cap to control the switch of the LED light.
Features
- PCF8574T Chip
- I2C interface
- 8-bit parallel port
- Potentiometer Backlight control
- LED jumper switch
- Default I2C address: 0x27
Gallery
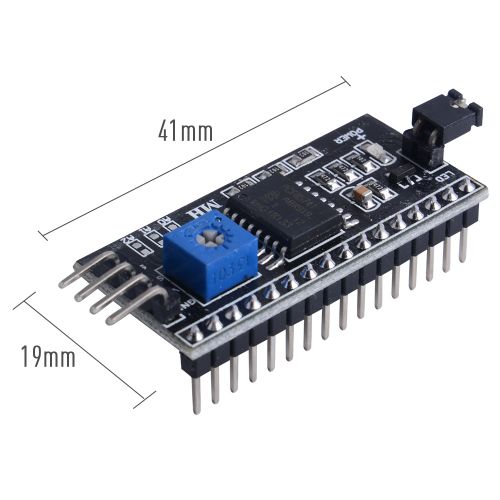
Dimenssion
Package Includes
- 1 x PCF8574T LCD Driver Board
Reference
- PCF8574T Chip Datasheet: File:PCF8574T Datasheet.pdf
- WiringPi: [ http://wiringpi.com/extensions/i2c-pcf8574/ ]
- telecnatron:[ https://telecnatron.com/articles/Utility-To-Control-1602-LCD-On-Raspberry-Pi-Via-A-PCF8574-I2C-Backpack-Module/index.html]
- Circuitbasics:[ https://www.circuitbasics.com/raspberry-pi-i2c-lcd-set-up-and-programming/ ]
Demo Code For Handle PCF8574T
- Download and reinstall wiringPi liberary
sudo apt -y purge wiringpi hash -r cd /tmp wget https://project-downloads.drogon.net/wiringpi-latest.deb sudo dpkg -i wiringpi-latest.deb
- C++ language
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <pcf8574.h>
using namespace std;
int main (int argc, char *argv[]){
printf("Raspberry Pi initializing...\n");
wiringPiSetup();
pcf8574Setup(100, 0x38);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){
pinMode(100 + i, OUTPUT);
}
int b=0;
while( 1==1 ){
printf("LOOP %u\n", b);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){
digitalWrite(100 + i, i==b ? 0 : 1);
}
b++;
if( b >= 8 ) b=0;
delay(1000);
}
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(100 + 0, 0);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(100 + 0, 1);
return 0;
}
- Compile and run it.
g++ pcf8574.cpp -o pcf8574 -lwiringPi -std=c++11 ./pcf8574
Python Demo Code
- Copy following code and save it as: I2C_LCD_driver.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Original code found at:
# https://gist.github.com/DenisFromHR/cc863375a6e19dce359d
"""
Compiled, mashed and generally mutilated 2014-2015 by Denis Pleic
Made available under GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
# Modified Python I2C library for Raspberry Pi
# as found on http://www.recantha.co.uk/blog/?p=4849
# Joined existing 'i2c_lib.py' and 'lcddriver.py' into a single library
# added bits and pieces from various sources
# By DenisFromHR (Denis Pleic)
# 2015-02-10, ver 0.1
"""
# i2c bus (0 -- original Pi, 1 -- Rev 2 Pi)
# I2CBUS = 0
I2CBUS = 1
# LCD Address
#ADDRESS = 0x3f
ADDRESS = 0x27
import smbus
from time import sleep
class i2c_device:
def __init__(self, addr, port=I2CBUS):
self.addr = addr
self.bus = smbus.SMBus(port)
# Write a single command
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.bus.write_byte(self.addr, cmd)
sleep(0.0001)
# Write a command and argument
def write_cmd_arg(self, cmd, data):
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.addr, cmd, data)
sleep(0.0001)
# Write a block of data
def write_block_data(self, cmd, data):
self.bus.write_block_data(self.addr, cmd, data)
sleep(0.0001)
# Read a single byte
def read(self):
return self.bus.read_byte(self.addr)
# Read
def read_data(self, cmd):
return self.bus.read_byte_data(self.addr, cmd)
# Read a block of data
def read_block_data(self, cmd):
return self.bus.read_block_data(self.addr, cmd)
# commands
LCD_CLEARDISPLAY = 0x01
LCD_RETURNHOME = 0x02
LCD_ENTRYMODESET = 0x04
LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL = 0x08
LCD_CURSORSHIFT = 0x10
LCD_FUNCTIONSET = 0x20
LCD_SETCGRAMADDR = 0x40
LCD_SETDDRAMADDR = 0x80
# flags for display entry mode
LCD_ENTRYRIGHT = 0x00
LCD_ENTRYLEFT = 0x02
LCD_ENTRYSHIFTINCREMENT = 0x01
LCD_ENTRYSHIFTDECREMENT = 0x00
# flags for display on/off control
LCD_DISPLAYON = 0x04
LCD_DISPLAYOFF = 0x00
LCD_CURSORON = 0x02
LCD_CURSOROFF = 0x00
LCD_BLINKON = 0x01
LCD_BLINKOFF = 0x00
# flags for display/cursor shift
LCD_DISPLAYMOVE = 0x08
LCD_CURSORMOVE = 0x00
LCD_MOVERIGHT = 0x04
LCD_MOVELEFT = 0x00
# flags for function set
LCD_8BITMODE = 0x10
LCD_4BITMODE = 0x00
LCD_2LINE = 0x08
LCD_1LINE = 0x00
LCD_5x10DOTS = 0x04
LCD_5x8DOTS = 0x00
# flags for backlight control
LCD_BACKLIGHT = 0x08
LCD_NOBACKLIGHT = 0x00
En = 0b00000100 # Enable bit
Rw = 0b00000010 # Read/Write bit
Rs = 0b00000001 # Register select bit
class lcd:
#initializes objects and lcd
def __init__(self):
self.lcd_device = i2c_device(ADDRESS)
self.lcd_write(0x03)
self.lcd_write(0x03)
self.lcd_write(0x03)
self.lcd_write(0x02)
self.lcd_write(LCD_FUNCTIONSET | LCD_2LINE | LCD_5x8DOTS | LCD_4BITMODE)
self.lcd_write(LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | LCD_DISPLAYON)
self.lcd_write(LCD_CLEARDISPLAY)
self.lcd_write(LCD_ENTRYMODESET | LCD_ENTRYLEFT)
sleep(0.2)
# clocks EN to latch command
def lcd_strobe(self, data):
self.lcd_device.write_cmd(data | En | LCD_BACKLIGHT)
sleep(.0005)
self.lcd_device.write_cmd(((data & ~En) | LCD_BACKLIGHT))
sleep(.0001)
def lcd_write_four_bits(self, data):
self.lcd_device.write_cmd(data | LCD_BACKLIGHT)
self.lcd_strobe(data)
# write a command to lcd
def lcd_write(self, cmd, mode=0):
self.lcd_write_four_bits(mode | (cmd & 0xF0))
self.lcd_write_four_bits(mode | ((cmd << 4) & 0xF0))
# write a character to lcd (or character rom) 0x09: backlight | RS=DR<
# works!
def lcd_write_char(self, charvalue, mode=1):
self.lcd_write_four_bits(mode | (charvalue & 0xF0))
self.lcd_write_four_bits(mode | ((charvalue << 4) & 0xF0))
# put string function with optional char positioning
def lcd_display_string(self, string, line=1, pos=0):
if line == 1:
pos_new = pos
elif line == 2:
pos_new = 0x40 + pos
elif line == 3:
pos_new = 0x14 + pos
elif line == 4:
pos_new = 0x54 + pos
self.lcd_write(0x80 + pos_new)
for char in string:
self.lcd_write(ord(char), Rs)
# clear lcd and set to home
def lcd_clear(self):
self.lcd_write(LCD_CLEARDISPLAY)
self.lcd_write(LCD_RETURNHOME)
# define backlight on/off (lcd.backlight(1); off= lcd.backlight(0)
def backlight(self, state): # for state, 1 = on, 0 = off
if state == 1:
self.lcd_device.write_cmd(LCD_BACKLIGHT)
elif state == 0:
self.lcd_device.write_cmd(LCD_NOBACKLIGHT)
# add custom characters (0 - 7)
def lcd_load_custom_chars(self, fontdata):
self.lcd_write(0x40);
for char in fontdata:
for line in char:
self.lcd_write_char(line)
- Create a file named: lcd1602.py and paste following code:
import I2C_LCD_driver
from time import *
mylcd = I2C_LCD_driver.lcd()
# There are 16 character that you can put on the screen and 2 lines avaliable.
mylcd.lcd_display_string("00000000000000000", 1, 0)
mylcd.lcd_display_string("00000000000000000", 2, 0)
- Run it.
python lcd1602.py
Application Scenario
- Control-Any-Devices-Using-Raspberry-PI-and-PCF8574: [ https://www.instructables.com/id/Control-Any-Devices-Using-Raspberry-PI-and-PCF8574/ ]
- I2C-1602-LCD: [1]
Keywords
- PCF8574T, LCD1602, driver board, LCD driver board